Cruise Ship Engine: The Heart of the Ocean Giants
Cruise ships are like floating cities, packed with restaurants, pools, and theaters. But have you ever wondered how these massive ships keep everything running smoothly? The answer lies in the cruise ship engine—a powerful machine responsible for moving the ship and producing electricity for everything on board, from air conditioning to lighting. These engines are feats of engineering, working tirelessly to ensure a smooth journey for passengers and crew. Let’s explore the fascinating world of cruise ship engines in an easy-to-understand way.
What Types of Engines Do Cruise Ships Use?
Most cruise ships use diesel-electric engines, a type of engine that works a bit differently from your car. Instead of directly turning the ship’s propellers, these engines produce electricity, which powers electric motors to move the ship. This method, called electric propulsion, is quieter and more efficient than traditional engines.
Some modern cruise ships also use gas turbines, which are similar to the engines in jet planes. While gas turbines are lighter and can produce more power, they use a lot of fuel, so they’re less common. Ships like those operated by Royal Caribbean sometimes use a combination of diesel-electric and gas turbines to get the best mix of power and efficiency.
How Big Are Cruise Ship Engines?
Imagine a machine so big it can fill a small building—that’s how large a cruise ship engine can be. These engines weigh hundreds of tons and are designed to handle the enormous energy demands of a ship carrying thousands of passengers and crew.
The cruise ship engine room, where these engines are located, is a maze of machinery, wires, and pipes. It’s not just about propulsion—these engines also produce electricity to power everything on the ship, from lighting to air conditioning. The heat generated by the engines is even used to warm water or create additional energy, ensuring nothing goes to waste.
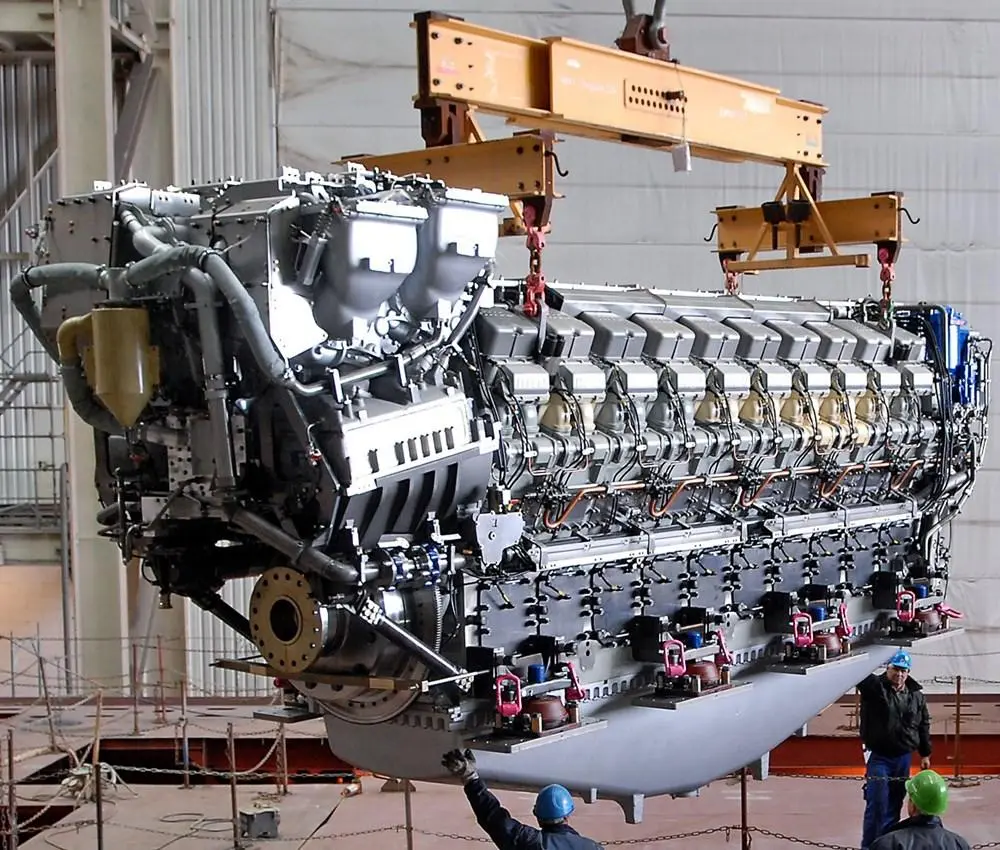

How Much Horsepower Does a Cruise Ship Engine Have?
One cruise ship engine can generate over 100,000 horsepower. That’s like the power of 333 sports cars working together! This incredible strength is what allows these floating cities to move smoothly across the water, even when carrying as much weight as several skyscrapers combined.
With multiple diesel engines working together, the ship has enough power to keep everything running—not just propulsion, but also electrical power for restaurants, pools, and even the Wi-Fi system.
Where Are Cruise Ship Engines Located?
The engines are usually located deep in the hull, at the bottom of the ship. This placement keeps the ship stable and protects the engines from waves and rough seas. The control room, located near the engine room, is where engineers monitor how the engines work, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
The design of modern cruise ships makes it possible for passengers to enjoy their trip without ever noticing the work happening below deck. The quiet hum of the engines is a testament to how efficiently they operate.
How Are Cruise Ships Powered?
Cruise ships don’t just use their engines for propulsion—they also need power for a wide range of systems on board. The engines produce electricity, which powers everything from lighting to air conditioning. This electricity is also used to drive electric propulsion systems, which move the ship quietly and efficiently.
Some ships, like those in the Royal Caribbean fleet, use advanced technology to reduce emissions. These include scrubbers and cleaner fuels, which help minimize the environmental impact of such large engines.
Why Do Cruise Ships Use Diesel-Electric Engines?
Diesel-electric engines are the gold standard for cruise ships because they’re reliable, powerful, and efficient. These engines work by burning fuel to generate electricity, which then powers the ship’s motors.
A big advantage is how flexible this system is. If one engine stops working, the others can take over, ensuring there’s no disruption to the ship’s operations. Plus, diesel-electric engines are quieter than older systems, making the journey more comfortable for everyone on board.
What Fuel Do Cruise Ships Use?
Most cruise ships run on marine diesel oil (MDO) or heavy fuel oil (HFO), which are thicker and cheaper than regular gasoline. However, these fuels produce a lot of emissions. To combat this, modern cruise ships are starting to use cleaner options like liquefied natural gas (LNG), which burns cleaner and produces fewer pollutants.
Efforts to reduce emissions are becoming a priority in the cruise industry. Ships are now equipped with advanced technologies to capture and clean exhaust gases, helping protect the environment while keeping engines running efficiently.
What Happens If a Cruise Ship Engine Fails?
Engine failure sounds like a big deal, but cruise ships are built with backups to handle such situations. Most ships have multiple engines, so if one stops working, the others can keep the ship moving. Additionally, engineers in the control room constantly monitor the engines, ensuring any problem is addressed immediately.
These safety measures ensure that passengers and crew are never at risk, even in the rare case of engine trouble. Modern cruise ships are designed to keep everything running smoothly, no matter what.
How Fast Can a Cruise Ship Go?
Most cruise ships travel at about 20 to 25 miles per hour (18 to 22 knots). That might not sound fast, but it’s perfect for a smooth, leisurely journey. Some ships can go faster when needed, especially for specific itineraries or tight schedules.
The speed of the ship depends on the engines and the weight it’s carrying. Diesel engines are powerful enough to push these floating cities across the ocean without breaking a sweat.
The Most Powerful Cruise Ship Engines in the World
Some of the most impressive engines belong to ships like the Oasis-class vessels from Royal Caribbean. These giants use multiple diesel-electric engines to generate over 100,000 horsepower, enough to power a small town!
Another remarkable example is the Queen Mary 2, which combines gas turbines and diesel engines for both power and speed. These engineering marvels show just how advanced cruise ship engines have become.
Conclusion
The cruise ship engine is truly the heart of these floating cities, providing the power needed to move, light, and operate the entire vessel. From diesel-electric engines to advanced systems that reduce emissions, these engines are a blend of power and innovation.
Next time you’re on a cruise, think about the incredible machines working tirelessly behind the scenes to make your trip unforgettable. The cruise ship engine isn’t just a machine—it’s the silent hero of every voyage.
Also Read This: What Is Steam System? How Does It Work?