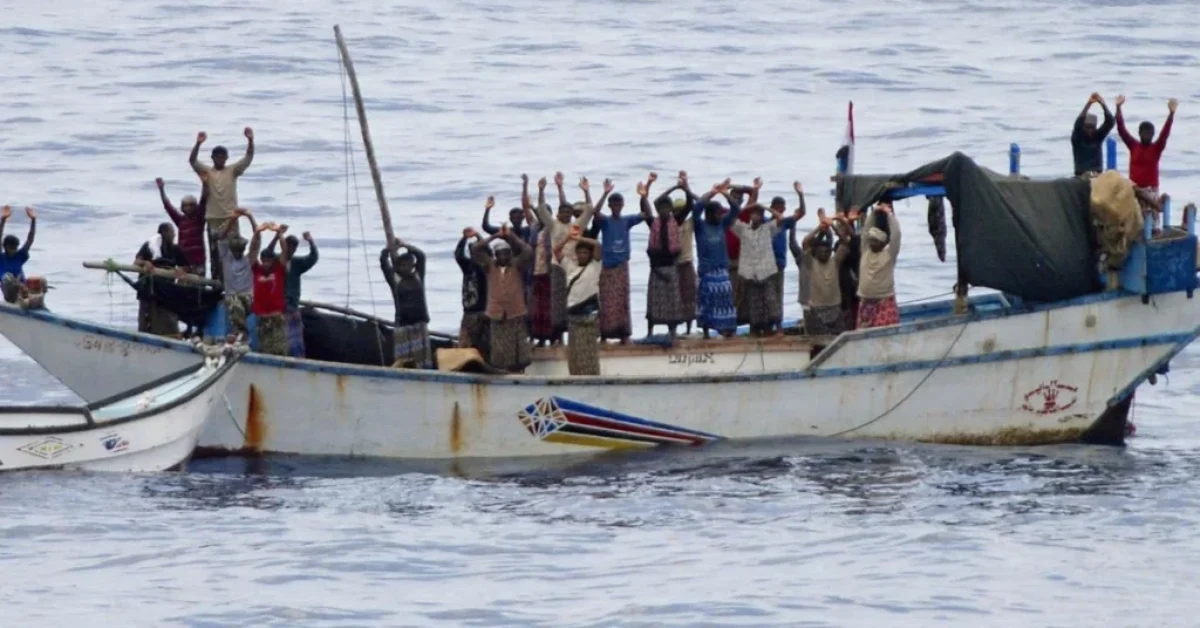
Are There Modern-Day Pirates?
When people hear the word “pirate,” they often imagine a swashbuckling figure with a parrot on their shoulder and a treasure map in their hand. But pirates aren’t just a thing of the past—they exist today, and they’re still causing problems in many parts of the world. Modern-day pirates might not look like they stepped out of a movie, but they can be just as dangerous. Let’s dive into what modern piracy looks like, where it happens, and what’s being done to stop it.
What Defines Modern Pirates?
Modern pirates are different from the ones we read about in history books. Instead of looking for gold, they’re after more practical things—money, cargo, and sometimes even entire ships. These pirates typically work in groups and have one goal: to make a quick profit. Unlike their historical counterparts, modern pirates use speedboats instead of ships with sails. They also carry weapons like AK-47s, grenades, and even rocket launchers, making them a serious threat to anyone on the water.
What sets modern pirates apart is their focus on technology. They often use GPS to track ships, and radios to communicate with their crews. Instead of swords and cannons, today’s pirates rely on guns and other modern weapons to take control of ships. Their methods may be different, but the risk they pose is very real.
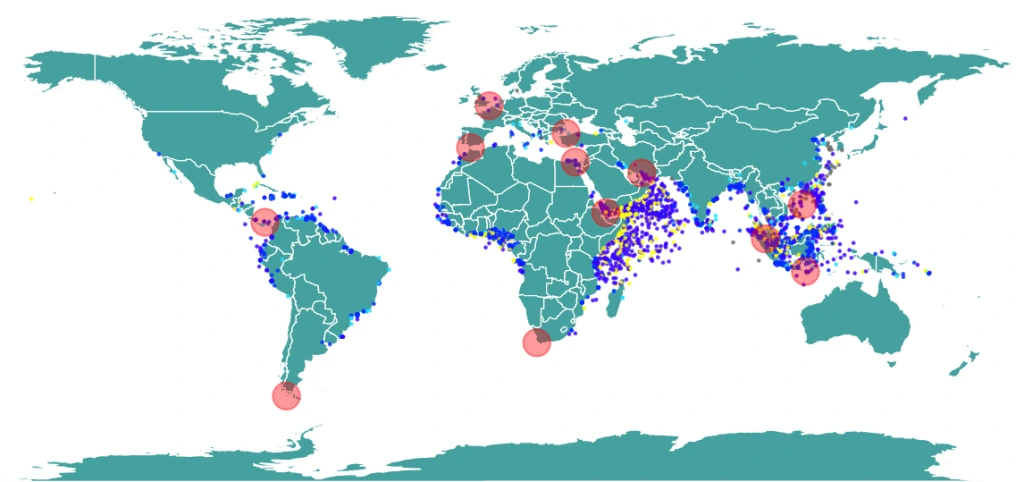
Where Are Modern Pirates Active?
Piracy is not a global problem—there are certain areas where it’s much more common. Some of the key regions include:
- The Horn of Africa (Somalia): Somalia is one of the most notorious places for modern piracy. Pirates there target large cargo ships and oil tankers passing through the busy shipping lanes of the Indian Ocean. Piracy in Somalia has declined in recent years, but it’s still a major concern.
- Southeast Asia: The waters near Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines are another piracy hotspot. Pirates here often target smaller boats, like fishing vessels, and sometimes hijack them for ransom.
- The Gulf of Guinea (West Africa): Recently, this region has seen a big rise in piracy. Pirates in the Gulf of Guinea are known for kidnapping crew members and demanding large sums of money for their release.
- The Caribbean and South America: While not as common, there have been reports of piracy near Venezuela and other parts of the Caribbean. These pirates mostly attack smaller vessels, like yachts.
So, if you’re sailing in these areas, pirates could be a real threat. However, some regions are more dangerous than others, and many ships take extra precautions when traveling through these waters.
Who Are Modern Pirates Today?
Modern pirates don’t all fit one description. They come from different backgrounds and have different reasons for turning to piracy. Here are a few types of modern pirates:
- Desperate Fishermen: In places like Somalia, some pirates used to be fishermen. After their fishing industry collapsed due to foreign competition and illegal fishing, they turned to piracy to survive.
- Organized Criminals: Some modern pirates are part of larger criminal organizations. These groups are highly organized and may have connections to other illegal activities, like drug smuggling or human trafficking.
- Local Gangs: In some regions, piracy is a smaller-scale operation run by local gangs. These pirates often target smaller boats or ships near the coast.
No matter what their background, most pirates are motivated by money. Whether it’s stealing valuable cargo, holding ships for ransom, or kidnapping crew members, the goal is usually to get rich quickly.
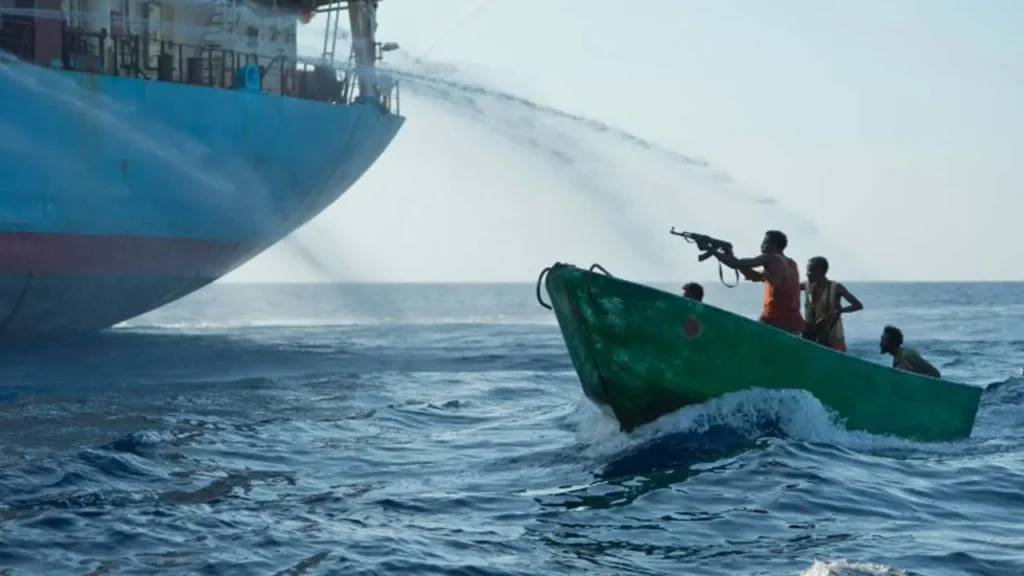
How Do Modern Pirates Operate?
Modern pirates have a variety of methods to attack ships. Some of the most common tactics include:
- Speedboat Attacks: Pirates often use small, fast boats to approach larger ships. These speedboats are difficult to spot and can move quickly through the water, making it easy for pirates to sneak up on unsuspecting vessels.
- Boarding Ships: Once pirates are close enough, they use ladders, grappling hooks, or even climb ropes to get on board. They may threaten the crew with weapons to take control of the ship.
- Holding Hostages: In many cases, modern pirates don’t want the ship itself—they want to hold the crew for ransom. They may kidnap crew members and demand large sums of money from the shipping company for their release.
- Stealing Cargo: Pirates may also steal the cargo on board, especially if it’s something valuable like oil or electronics. This can happen quickly, with pirates unloading the cargo and disappearing before the authorities can respond.
These tactics allow pirates to strike quickly and make their escape before help can arrive, making them a dangerous threat on the seas.

Modern Pirates vs. Historical Pirates
So, how do modern pirates compare to the famous pirates of the past? Here are some key differences:
- Motivation: While historical pirates were often searching for treasure, today’s pirates are more focused on money, whether it’s through ransom or stolen goods.
- Technology: Old-time pirates relied on swords, cannons, and sailing ships. Modern pirates use speedboats, GPS, and guns to get the job done.
- Pirate Code: Historical pirates often followed a code of conduct, dividing treasure among the crew. Modern pirates don’t follow any such code, and they tend to work in more flexible, often more violent, groups.
- Appearance: Forget the eye patches and pirate hats—modern pirates look just like regular people. They might be wearing jeans and a T-shirt, but they’re just as dangerous.
The world of piracy has changed, but one thing has stayed the same: the desire to steal and make a profit.
Is Piracy Increasing Today?
In some parts of the world, piracy has decreased, like off the coast of Somalia. This is thanks to increased international efforts, like having navy ships patrol the area and shipping companies paying for armed security on board. However, in other places, piracy is on the rise. The Gulf of Guinea is now considered one of the most dangerous places for piracy, and attacks in Southeast Asia remain a concern.
Global piracy is a bit of a moving target—it goes up in some areas and down in others. But one thing is clear: as long as there’s money to be made, piracy isn’t going away anytime soon.
Who Do Pirates Target?
Modern pirates are strategic about who they target. They usually go after:
- Cargo Ships: These ships carry valuable goods like oil, electronics, and food, making them a prime target for pirates.
- Fishing Vessels: In some areas, pirates steal from local fishermen or hijack their boats for ransom.
- Tanker Ships: Oil tankers are often targeted because of the high value of the cargo on board.
- Yachts and Private Boats: In areas like the Caribbean, pirates sometimes target smaller private boats, especially if they think the owners have wealth.
Pirates choose targets that they think will give them the most reward for the least effort. A ship with no armed guards or protection is an easy mark.
How Do Governments Fight Pirates?
Fighting modern piracy takes a lot of cooperation between countries. Here’s how governments are tackling the problem:
- Naval Patrols: Countries like the United States and the UK send their navy ships to patrol dangerous waters, especially near Somalia and the Gulf of Guinea. These patrols can stop pirate attacks or rescue ships that have already been captured.
- International Agreements: Many countries have signed agreements to work together against piracy. This means they share information and resources to track and stop pirates.
- Private Security: Some shipping companies hire private security teams to protect their ships. These teams are trained to spot pirate threats and defend the ship if necessary.
Even with all these efforts, pirates still find ways to attack. But governments and shipping companies are working hard to make the seas safer.
The Role of Technology in Modern Piracy
Technology plays a huge role in both helping and stopping modern pirates. Here’s how:
- Pirates Use Technology: Modern pirates use GPS to find ships and track their movements. They also use radios to communicate and coordinate attacks. Some pirates even use high-tech equipment to jam a ship’s radar and stay hidden until it’s too late for the crew to react.
- Ships Fight Back with Technology: Many ships now have advanced security systems. Some can spray attackers with high-pressure water or release loud sound waves to scare pirates away. Others use radars and cameras to detect pirates long before they get close.
Both sides are using tech to their advantage, but the fight against piracy is constantly evolving.
How Dangerous Are Modern Pirates?
Modern pirates are extremely dangerous. They carry guns, grenades, and other weapons, and they aren’t afraid to use them. If a crew tries to fight back, pirates often respond with violence. Even if the pirates don’t intend to harm anyone, the stress and fear of being taken hostage can have a huge impact on the people on board.
While some pirate attacks end peacefully, with crews being released after a ransom is paid, others can turn violent quickly. Modern pirates can be unpredictable, and that’s what makes them so dangerous.
Why Do People Turn to Piracy?
Most people don’t wake up one day and decide to become pirates. There are usually deeper reasons behind it. Here are a few common ones:
- Economic Hardship: In many parts of the world, poverty and a lack of job opportunities push people into piracy. In Somalia, for example, overfishing destroyed the local fishing industry, and many people turned to piracy to make a living.
- Organized Crime: Some pirates are part of larger criminal organizations. These groups might see piracy as just one part of their illegal activities, like drug smuggling or trafficking.
- Lack of Law Enforcement: In regions with weak governments or little law enforcement, piracy can thrive because there’s no one to stop it. Pirates take advantage of these lawless areas to carry out their attacks without fear of being caught.
While piracy might be a way for some to make money, it’s still a serious crime that affects people’s lives.
What Happens to Captured Pirates?
When modern pirates are caught, they face serious consequences. Many countries, including the U.S. and the UK, have strict anti-piracy laws. Pirates who are caught can be put on trial and sent to prison for many years. Some might even face life sentences, depending on the severity of their crimes.
In some cases, pirates escape justice, especially in places where local governments don’t have the resources to arrest or prosecute them. But in many parts of the world, being caught means the end of a pirate’s career.
Conclusion
Modern piracy is a serious issue, but it’s not as well-known as the pirates from the past. Today’s pirates use technology, weapons, and quick attacks to steal cargo, hold hostages, and sometimes cause harm. They operate in dangerous regions like Somalia, Southeast Asia, and West Africa, and they continue to pose a threat to global trade and maritime safety.
Governments, navies, and shipping companies are working together to fight piracy, but it’s a constantly evolving battle. If there are valuable targets and economic hardship, piracy will remain a problem. Understanding how modern pirates operate and where they’re most active helps shine a light on a criminal world that’s still very much alive today.
